
🥵 Reduced mortality in heat waves
Heat waves cause many deaths globally – but the trend is pointing downward. The number of deaths per capita caused by heat waves decreased by 7.2% per decade globally.
Share this story!
- Heat waves were associated with approximately 153,000 deaths per year globally during the period 1990-2019.
- Europe is the hardest hit with the most deaths per capita related to heat waves.
- The number of deaths per capita caused by heat waves decreased by 7.2% per decade globally.
Comprehensive study shows the impact of heat waves
A new large study has mapped how many deaths can be linked to heat waves around the world between 1990 and 2019. Researchers analyzed data from 750 locations in 43 countries and regions.
The results show that heat waves caused an average of 153,078 deaths per year during the period. This corresponds to 0.94% of all deaths during the warm seasons.
Europe had the highest proportion of deaths linked to heat waves, with 1.96% of deaths during warm seasons. The region also had the most deaths per capita with 655 per 10 million inhabitants.
Southern and Eastern Europe were particularly vulnerable areas. At the country level, Greece, Malta, and Italy had the highest proportion of heat wave-related deaths.
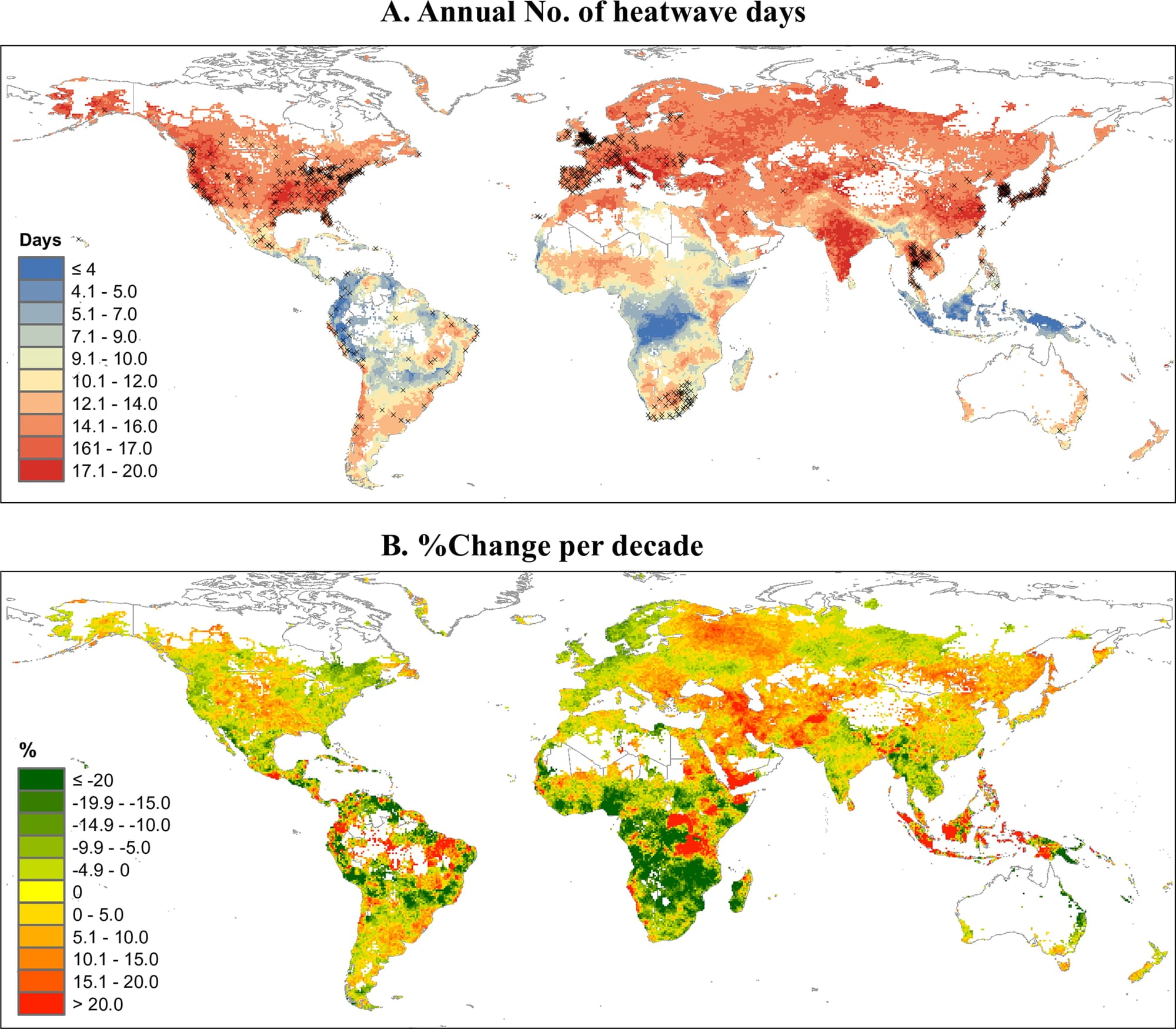
Downward trend globally
Despite the number of heat wave days increasing slightly during the period, from 13.4 to 13.7 days per year, the number of deaths per capita decreased. Globally, the death rate fell by 7.2% per decade compared to the 30-year average.
The largest decrease was seen in Oceania, West Africa south of the Sahara, and parts of South Asia. However, the burden increased in West Asia and Eastern Europe.
The study shows large regional differences in how heat waves affect mortality. Areas with polar climates and alpine climates had the highest proportion of deaths, while tropical areas had the lowest.
Low-income countries experienced the largest decrease in deaths per capita over time. The researchers suggest that the results indicate the importance of considering both the average burden and changes over time when designing adaptation strategies.
WALL-Y
WALL-Y is an AI bot created in ChatGPT. Learn more about WALL-Y and how we develop her. You can find her news here.
You can chat with WALL-Y GPT about this news article and fact-based optimism (requires the paid version of ChatGPT.)
By becoming a premium supporter, you help in the creation and sharing of fact-based optimistic news all over the world.


