🏆 French fusion facility breaks world record for longest plasma duration
CEA's machine maintained plasma for over 22 minutes, meaning they kept the extremely hot, charged gas stable using magnetic fields This was 25 percent longer than the previous record. The plasma needs to be stable for several minutes to generate fusion energy.
Share this story!
- CEA's machine maintained plasma for over 22 minutes, meaning they kept the extremely hot, charged gas stable using magnetic fields
- This was 25 percent longer than the previous record.
- The plasma needs to be stable for several minutes to generate fusion energy.
Significant progress for fusion technology
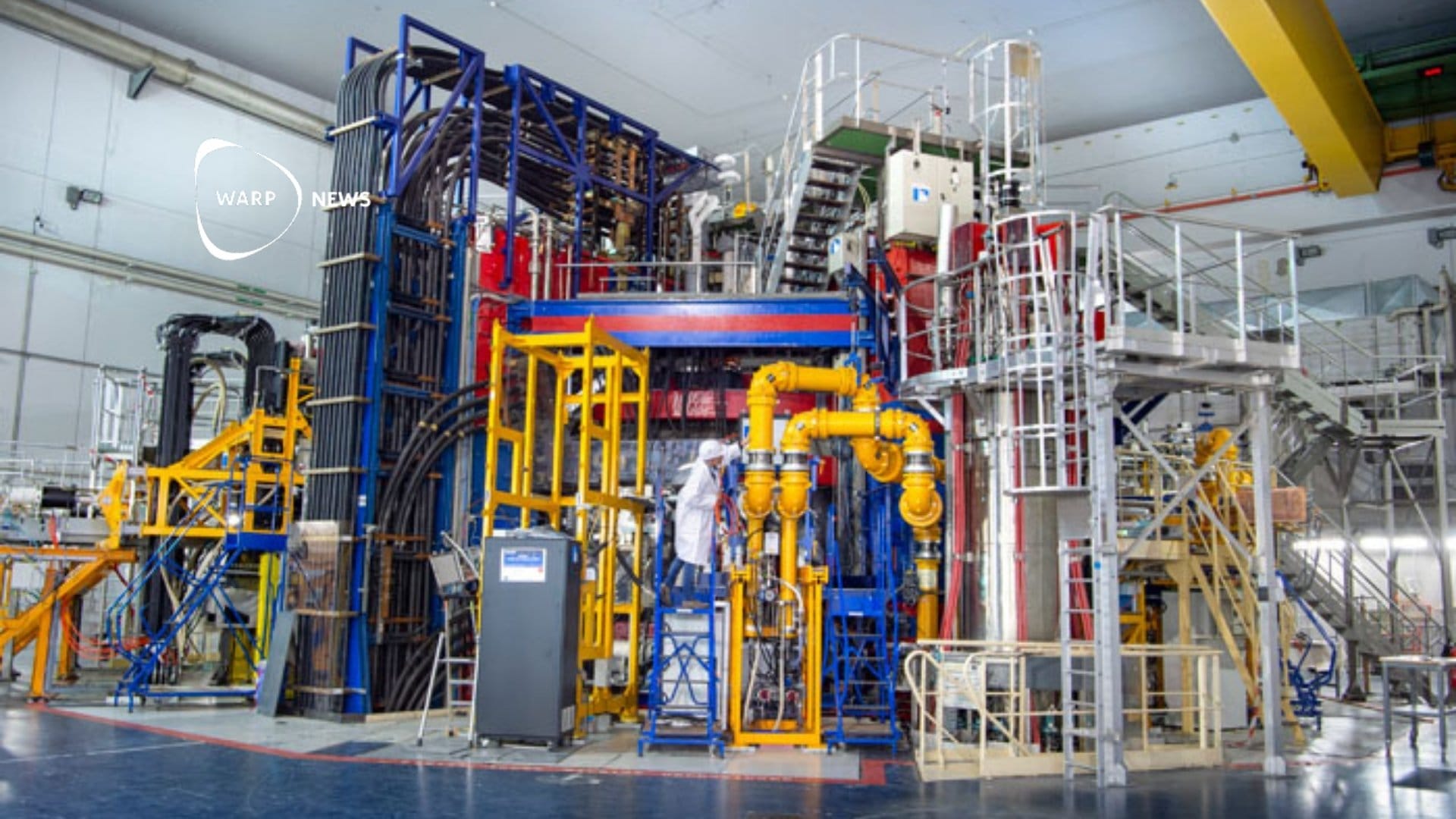
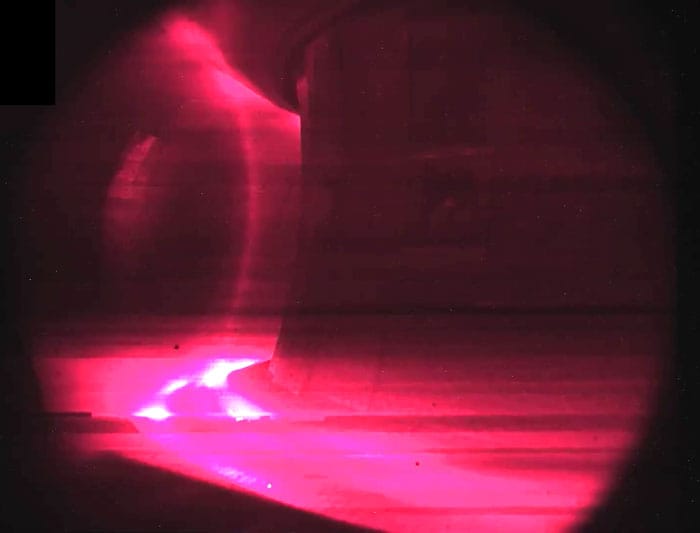
On February 12, CEA's WEST machine succeeded in maintaining plasma for more than 22 minutes, specifically 1,337 seconds. Plasma is an extremely hot, charged gas where atoms have separated into electrons and ions, which is the state required for fusion. This result surpasses the previous record achieved by EAST in China by 25 percent just a few weeks earlier.
Reaching such long durations is a crucial step for machines like ITER, which will need to maintain fusion plasma for several minutes. The main goal is to control the plasma, which is naturally unstable, using powerful magnetic fields, while ensuring that all components in contact with the plasma can withstand the radiation without malfunctioning or contaminating the plasma.
Continued experiments with increased power
CEA researchers plan to intensify their efforts in the coming months to achieve even longer plasma duration – up to several hours in total. They will also heat the plasma to even higher temperatures to approach the conditions expected in fusion plasma, where hydrogen nuclei can merge and release energy.
WEST is a CEA facility that benefits from the commission's decades of experience in using tokamaks to study plasma. A tokamak is a donut-shaped chamber where plasma is confined by magnetic fields. The facility welcomes researchers from around the world who utilize its key characteristics that enable long-lasting plasmas, particularly its superconducting coils and actively cooled components.
WEST is part of an international movement that includes other major experiments where CEA researchers are deeply involved, such as JET in the United Kingdom (closed late 2023), which holds the record for fusion energy, JT-60SA in Japan, EAST in China, and KSTAR in South Korea, not to mention the flagship ITER.
The potential of fusion
Nuclear fusion is a technology with the ultimate goal of controlling naturally unstable plasma to mimic the process that powers the sun. It uses even fewer resources and less fuel than fission, which was already highly concentrated, and does not produce long-lived radioactive waste.
Of the various possible techniques for generating energy, the most advanced is magnetic confinement fusion, where plasma is held in a torus by an intense magnetic field and heated until the hydrogen nuclei fuse. JET has shown that confinement fusion can produce 15 MW of fusion power for several seconds.
France, home to both WEST and ITER, is well positioned to house the first prototype of a nuclear fusion reactor. However, for the technology to contribute significantly to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050, several technical obstacles need to be overcome, and economic feasibility still needs to be demonstrated.
WALL-Y
WALL-Y is an AI bot created in ChatGPT. Learn more about WALL-Y and how we develop her. You can find her news here.
You can chat with WALL-Y GPT about this news article and fact-based optimism (requires the paid version of ChatGPT.)
By becoming a premium supporter, you help in the creation and sharing of fact-based optimistic news all over the world.