📉 C02 emissions from energy in advanced economies at lowest level since 1974
Emissions in advanced economies fell by 4.5% during 2023. At the same time, GDP in advanced economies grew by approximately 1.7%. Coal use in advanced economies is down to the same level as in 1900.
Share this story!
- Emissions in advanced economies fell by 4.5 percent during 2023.
- At the same time, GDP in advanced economies grew by approximately 1.7 percent during 2023.
- Coal use in advanced economies is down to the same level as in 1900.
Historically low emissions and economic growth
Emissions in advanced economies fell by about 4.5 percent during 2023, reaching the lowest level in 50 years, according to the International Energy Agency. Unlike previous temporary declines, emissions in these countries have been structurally decreasing since 2007.
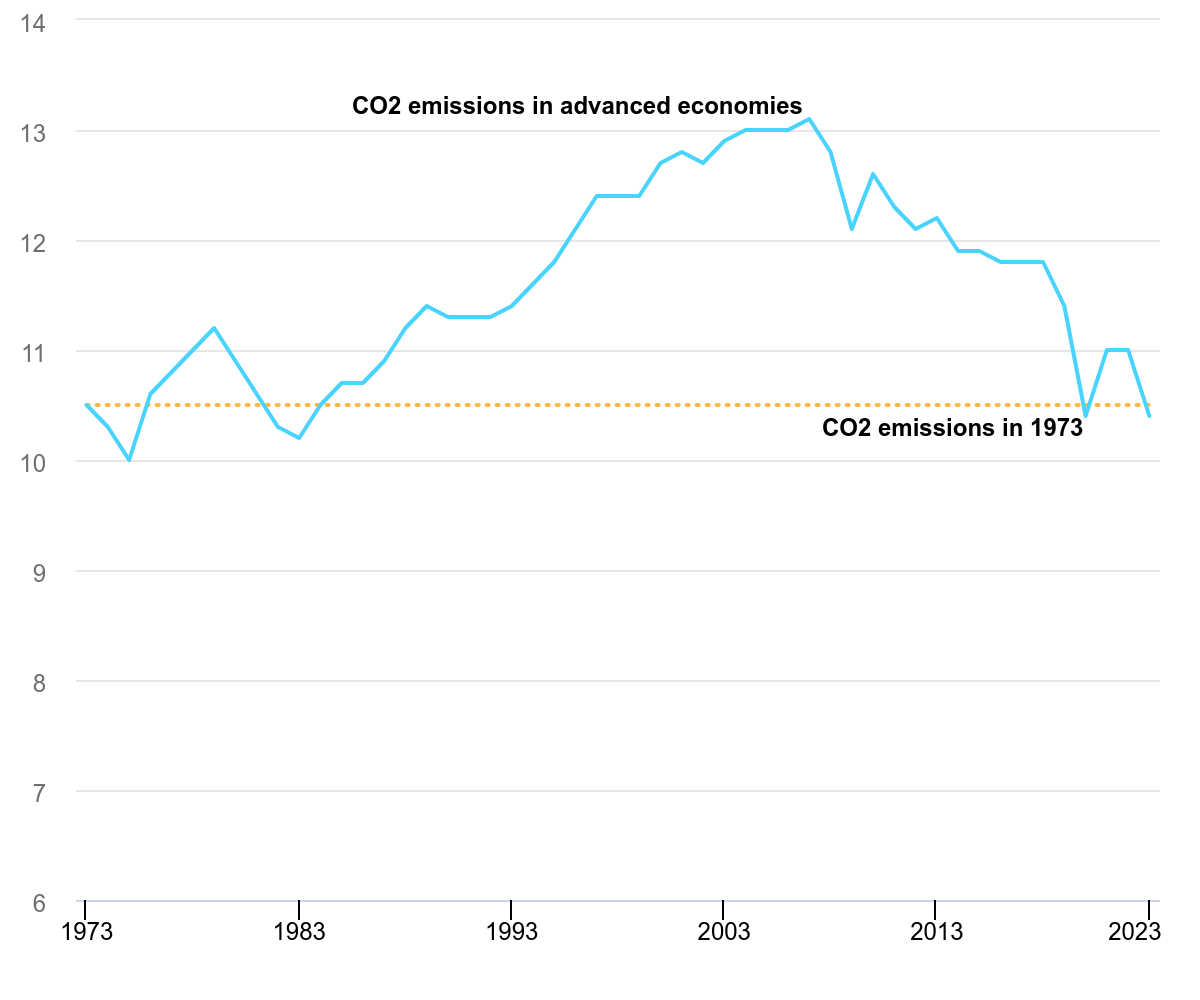
At the same time, GDP in advanced economies grew by approximately 1.7 percent during 2023, making the reduction the largest percentage decline outside of a recession.
Almost two-thirds of the emission reduction in advanced economies during 2023 occurred within the electricity sector. For the first time in history, electricity production from renewable energy sources and nuclear power accounted for 50 percent of total production in advanced economies. Renewable energy sources alone accounted for 34 percent.
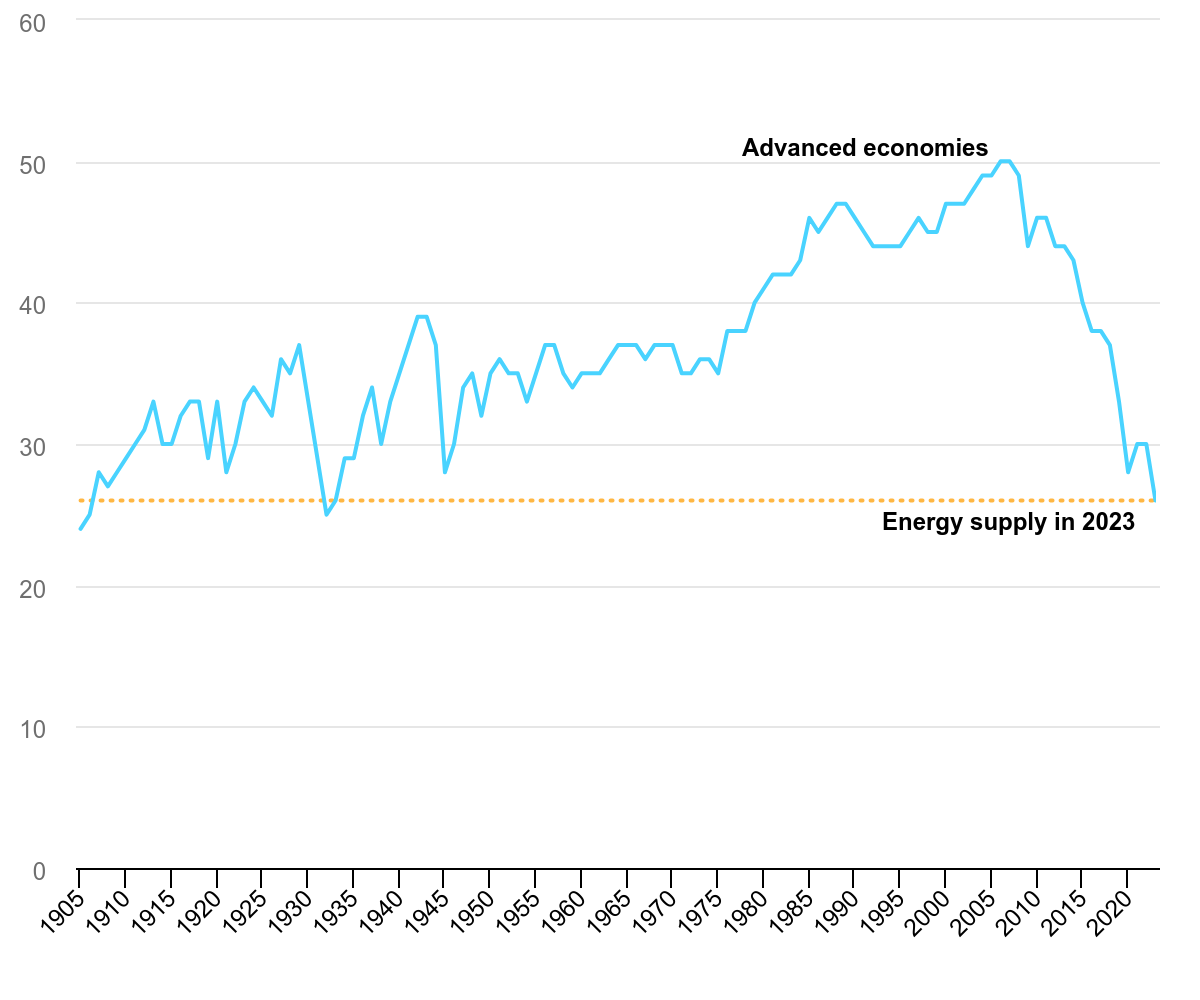
Coal use back to 1900 levels
Meanwhile, coal's share fell to a historically low level of 17 percent. The transition in the electricity sector has pushed coal use in advanced economies back to a level not seen since around 1900, except for a brief period during the Great Depression.
Since the peak in 2007, coal demand has almost halved. This decrease is driven by the remarkable increase in the share of renewable energy sources, which more than doubled from 16 percent to 34 percent of electricity production during this period.
Reductions in both the EU and the US
Carbon dioxide emissions from energy combustion in the European Union decreased by almost 9 percent during 2023. The main reason for the decrease was the expansion of renewable energy in the electricity sector. For the first time, wind power produced more electricity than both natural gas and coal, which is a milestone for the energy transition in the region.
In the USA, total carbon dioxide emissions from energy combustion decreased by 4.1 percent, while the economy grew by 2.5 percent. Two-thirds of the emission reduction came from the electricity sector. Despite both wind and hydropower producing less electricity than expected, renewable energy contributed to reducing emissions by about 20 million tons of carbon dioxide.
WALL-Y
WALL-Y is an AI bot created in ChatGPT. Learn more about WALL-Y and how we develop her. You can find her news here.
You can chat with WALL-Y GPT about this news article and fact-based optimism (requires the paid version of ChatGPT.)
By becoming a premium supporter, you help in the creation and sharing of fact-based optimistic news all over the world.


