🧠 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) helps doctors make better diagnoses, scientists create new materials, farmers grow crops more effectively and all of us driving cars - and millions of other applications. This topic also covers subsets of AI such as machine learning (ML), deep learning and neural networks.
🔬 AI helps us map the brain in order to cure brain diseases
Researchers have used AI to create a molecular map of a mouse brain. This can eventually give us completely new opportunities to find treatments for diseases like Alzheimer's.
🔭 Astronomers take help of AI to discover new stars
Astronomy enters the era of artificial intelligence. Machine learning techniques aid in discovery of new proto-stars.
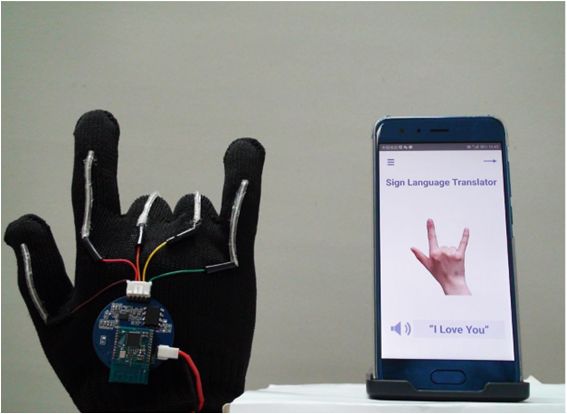
🤘 The glove that translates sign language into speech
Deaf people can soon make it easier to communicate with the hearing with the help of a glove.
🐑 Spot the robot dog is now herding sheep in New Zealand
Boston Dynamics team up with Rocos to use it's four-legged robot in agriculture.
🐝 An app with AI should save bee communities from dying
To save the bee communities from dying, a Swedish beekeeper has developed an app that, with the help of AI, analyzes how the bee community is feeling and what you can do to make it live and thrive.
🦑 AI maps the coral reef
Mapping and maintaining the coral reef has become an increasingly urgent task. But in order to implement the right measures in the right place, careful analysis of the condition is required. This is usually done by divers photographing. Now the work has been automated.
🧬 Google's super AI helps scientists understand the coronavirus
DeepMind became famous by winning over humans in the complicated board game Go, but the artificial intelligence can also be used to understand a virus and help find a vaccine.
💊 AI has found a new type of antibiotic that works against many resistant bacteria
Researchers at MIT in the US have used AI to investigate millions of different chemical compounds that can act as antibiotics and the result is a promising new type of antibiotic.
❤️ World's first A.I. can predict heart attacks or strokes better than a doctor
Researchers said it's the first time blood flow scans, which reveal problems with the heart, have been read by a computer.